Beta-Amyloid ELISA Kits
Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 – AD markers
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by the progressive accumulation of extracellular amyloid plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles. The most common species, Aβ1-40 and the most causative species of AD, Aβ1-42 constitute the many different Aβ-containing peptides detected in human cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and/or brain tissue. In addition, studies of circulating Aβ in blood have provided insights into Aβ equilibrium between the brain and the periphery with a few studies associating increased levels of plasma Aβ42 with AD at different stages.
Why choose our β-Amyloid ELISA Kits?
Our One-step assay kits to quantify human or mouse/rat beta-amyloid (1-40) or (1-42) peptides are optimized to detect beta-amyloid fragments with high sensitivity, specificity and reproducibility.
Convenient One-Step Assay Format
- Pre-coated and pre-blocked 96-well strip plate
- Ready-to-use substrate solution and other assay components
- One step assay (samples and detection antibodies are added simultaneously)
- 1 hour assay time at room temperature (excluding incubation)
High Sensitivity
- Detects as low as 2 pg/ml (13 fmoles/ml) of human beta-Amyloid (1-40) or (1-42)
Broad Dynamic Range
- 3.9-250 pg/ml of human beta-Amyloid (1-40) or (1-42) peptide
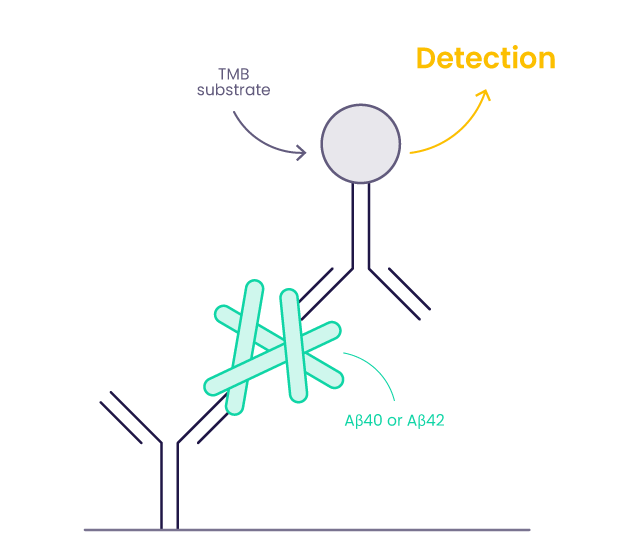
How does the beta-Amyloid detection work?
The kits are optimized to detect human beta-Amyloid (1-40) and (1-42) peptides in human brain lysate, transgenic mouse brain lysate, human cerebrospinal fluid, plasma, or saliva. Wells are pre-coated with monoclonal anti-beta-Amyloid (1-40) or (1-42) specific capture antibodies and blocked with a proprietary blocking solution. The amount of human beta-Amyloid (1-40) or (1-42) is quantified using ELISA. Ample materials and reagents are provided to perform 96 assays.
Why quantify β-Amyloid peptides in biological samples?
Quantification of human, mouse/rat β-Amyloid (1-40) or (1-42) peptide in biological samples including brain lysate, cerebrospinal fluid, plasma or serum marks thus an important aspect in detection, research and therapeutic development in the realm of how common Aβ species confer roles in AD and related neurofibrillar pathology.
Figure 1. Examples of ELISA standard curves, human (top) and mouse/rat (bottom).