COVID-19
SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle
Compared to SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 is better at evading the immune system, and in order to eradicate the current COVID-19 pandemic, it is of primary importance to study the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle including the virus-cell interaction and virion formation process.
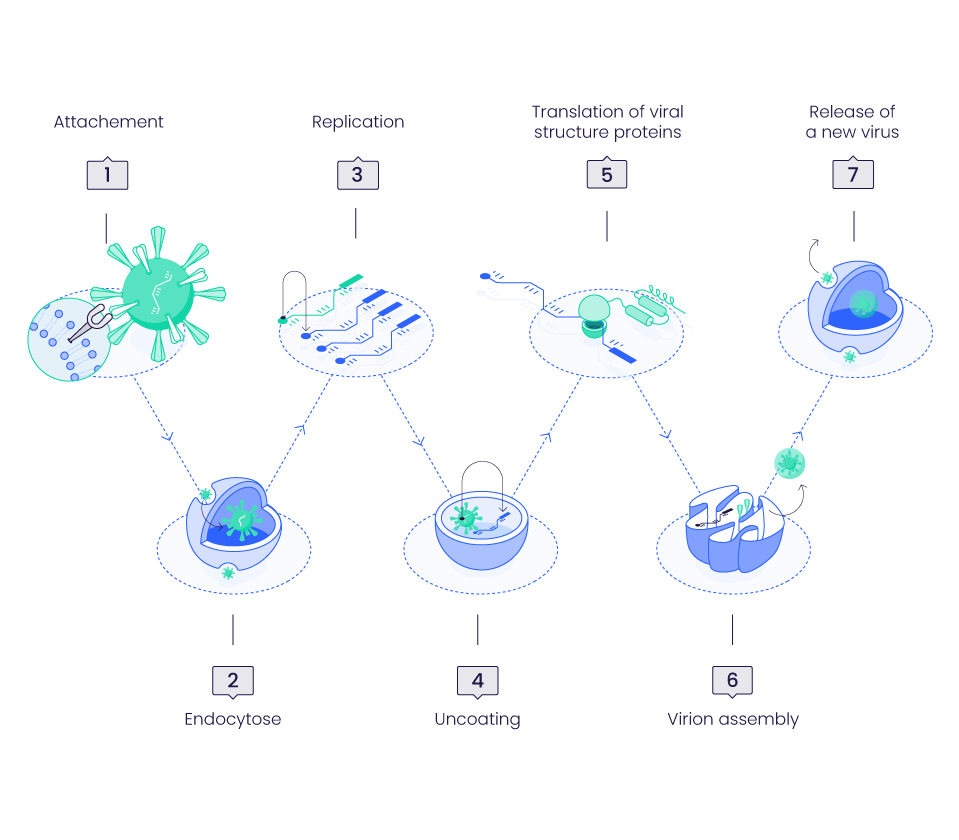
SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle step by step
Viral invasion starts in the upper respiratory tract. The SARS-CoV-2 virus particles link to the host cell ACE2 nasal epithelial cell receptors and pass down to the lungs before entering the other organ cells presenting ACE2 on their surface such as heart, kidney, intestine, testis and vascular endothelium. (1)
It has been shown that S proteins required a proteolytic cleavage to activate its potential to interact with ACE2. Furin, Cathepsins, trypsin, human airway trypsin-like proteases and transmembrane protease serine protease (1,2) have been identified to activate S proteins cleavage into S1 and S2 subunits.
SARS-CoV-2 Spike proteins (S proteins) require interaction with the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE2) receptors to enter the host cells by two ways: via endosomes or via fusion to plasma membrane.(3)
S1 segment binds the extra-cellular N-terminus of ACE2 while conformational changes in S2 subunit facilitate fusion between host cell membrane and viral envelope to initiate internalization of the virus/receptor complex by endocytose.(4)
Once released in the cell cytoplasm, the virus genome will be translated as a mRNA by the host cell machinery and generate essential enzymes (Nsp 1-16 complex) for RNA synthesis (incl. Nsp12 - RNA dependent RNA polymerase, RdRp; Nsp13 - zinc-binding helicase, HEL), proofreading (Nsp 14) and capping (Nsp14-Nsp16 complex). (4)
The assembly of the viral particles occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus of the host cells.
The generated virions release out of the cell by exocytosis or cell death. Some of the virions are breathed out to contaminate other people while other particles remain circulating in the body and interact with ACE2 receptors to cause the invasive infection.(4)
ACE2 Assay Kits
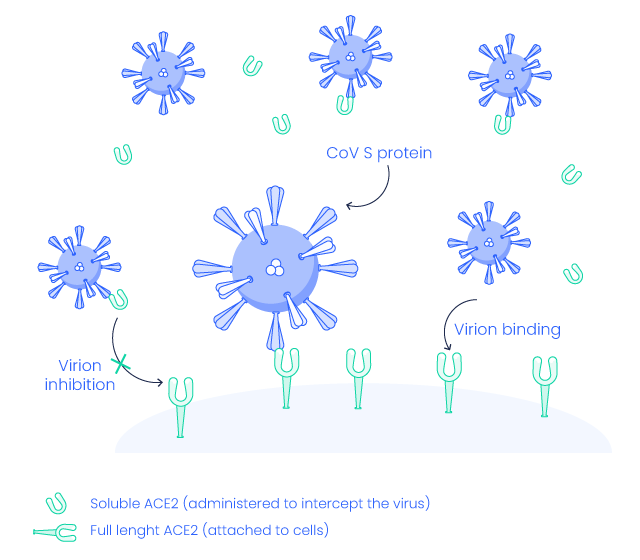
The extracellular domain of ACE2 has been demonstrated as a receptor for the spike (S) protein of SARS-CoV & SARS-CoV-2 but affinity between S glycoprotein and ACE2 is 10 to 20 fold higher in SARS-CoV-2 compared to SARS-CoV. Probably due to a polymorphinsm at 501T. This could explain why SARS-CoV-2 is more infectious than SARS-CoV (5,6)
The soluble form of ACE2 may act as a competitive inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 and could serve as a potentially novel therapeutic target to limit infection caused by SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19).
Cited in high impact journals, Our FRET assay detects the activity of sub-nanogram level of ACE2
Furin Assay Kits
The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 of some coronaviruses is cleaved at the S1/S2 boundary by furin(-like) proteases during transport of the newly assembled virions through the secretory pathway.
Screening for furin inhibitors observed with furin-dependent viral replication may present as a potential target for drug design.
Select your tools
Choose the products that best suit your COVID-19 life cycle research and drug discovery needs
Peptides play various roles in the Coronavirus physiology. For example, certain sequences can serve as substrates for the proteolytic machinery of the viral fusion system, epitopes for antibody screening, targets within receptor binding or fusion domains or have inhibitory roles in viral autophagy.
The SARS-CoV viral proteins have been identified as targets of several host proteases, among which Furin, 3CLpro (3C-like viral protease) and Cathepsins (B, L) play roles.
Based on this we give you access to a series of protease assay kits to better understand the SARS-CoV-2 mechanism of action.
Besides ready-to-use catalog peptides from SARS-CoV-2 proteins including critical peptide domains/regions or peptide substrates, we can synthesize custom peptides from simple to highly complex sequences.
We also offer custom manufacturing of Critical Raw Material (CRM) peptides for demanding applications.
| Catalog SARS-CoV-2 peptides | Order now |
|---|---|
| Custom peptide synthesis | Learn more |
| Critical raw material peptides | Learn more |
References
1) The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues.
F. Hikmet, L. Mear, M. Uhlen, C. Lindskog.
bioRxiv, (2020); DOI: 10.1101/2020.03.31.016048.
2) A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin.
P. Zhou, X.L. Yang, X.G. Wang, B. Hu, L. Zhang, W. Zhang, H.R. Si, Y. Zhu, B. Li, C.L. Huang, H.D. Chen, J. Chen, Y. Luo, H. Guo, R.D. Jiang, M.Q. Liu, Y. Chen, X.R. Shen, X. Wang, X.S. Zheng, K. Zhao, Q.J. Chen, F. Deng, L.L. Liu, B. Yan, F.X. Zhan, Y.Y. Wang, G.F. Xiao, Z.L. Shi.
Nature 579 (7798) (2020) 270–273 – DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
3) A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin.
P. Zhou, X.L. Yang, X.G. Wang, B. Hu, L. Zhang, W. Zhang, H.R. Si, Y. Zhu, B. Li, C.L. Huang, H.D. Chen, J. Chen, Y. Luo, H. Guo, R.D. Jiang, M.Q. Liu, Y. Chen, X.R. Shen, X. Wang, X.S. Zheng, K. Zhao, Q.J. Chen, F. Deng, L.L. Liu, B. Yan, F.X. Zhan, Y.Y. Wang, G.F. Xiao, Z.L. Shi.
Nature 579 (7798) (2020) 270–273 – DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
4) Drugs targeting various stages of the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle: Exploring promising drugs for the treatment of Covid-19.
Ramarao Poduri, Gaurav Joshi, Gowraganahalli Jagadeesh.
Cellular Signalling 74 (2020) 109721 - DOI : 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109721
5) Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses.
Letko M, Marzi A, Munster V.
Nat Microbiol. 2020 Apr;5(4):562-569 - DOI: 10.1038/s41564-020-0688-y
6) Investigation of the genetic variation in ACE2 on the structural recognition by the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2).
Guo X, Chen Z, Xia Y, Lin W, Li H.
J Transl Med. 2020 Aug 24;18(1):321 - DOI: 10.1186/s12967-020-02486-7